How to develop Self-control: A Comprehensive Guide to Gaining Self-Control
Self-control is a learned skill crucial for well-being, yet building willpower takes conscious effort. This in-depth guide outlines science-backed strategies to help you better regulate impulses and achieve goals.
Self-control development necessitates concerted effort over the long term. While determined by genes and environment outside individual sway, committed daily undertakings across salient topics can strengthen this important existence ability.
Core concepts regarding How to develop Self-control comprise things like self-control description, influences on capacity like limited willpower resources and strain, developing impulse authority via pre-commitment, and the like. Additionally, topics of mastering emotions, gaining goals through resolve, and backing self-control evolution were discussed to provide an extensive toolbox promoting self-control growth.
Through techniques like predetermination, temptation bonding, and delaying gratification, cultivating stronger control over yearnings can be achieved. Supplementing this, applying insight like craving reframing, portion authority, dropping all-or-nothing mentality, and majoring on accomplishments rather than excellent promotes purposeful behaviors aligned with highest priorities.
Mastering sentiments requires tact like making mental notes of sentiments non-judgmentally, challenging irrational views, and pressure direction. Enlisting outlets, limiting volatile companions, and forgiving kindly aids sentiment sway no longer weakening willpower.
Backing expands through perspectives like thinking advancement is achievable with training instead of a unchanging endowment. Notably tracking triumphs, honoring little achievements, limiting unfavorable impacts, and discussing targets supportively retains one responsible over the long term.
While impacted some by constitution and childhood, self-control enhancement through consistent practice of techniques addressed empowers larger management over inner impulses through way of life changes. Moving ahead, refining methods and tracking advancement unlocks tremendous unrealized capacity to form each instant and ultimately to advantage most of invaluable present.
What is Self-Control?
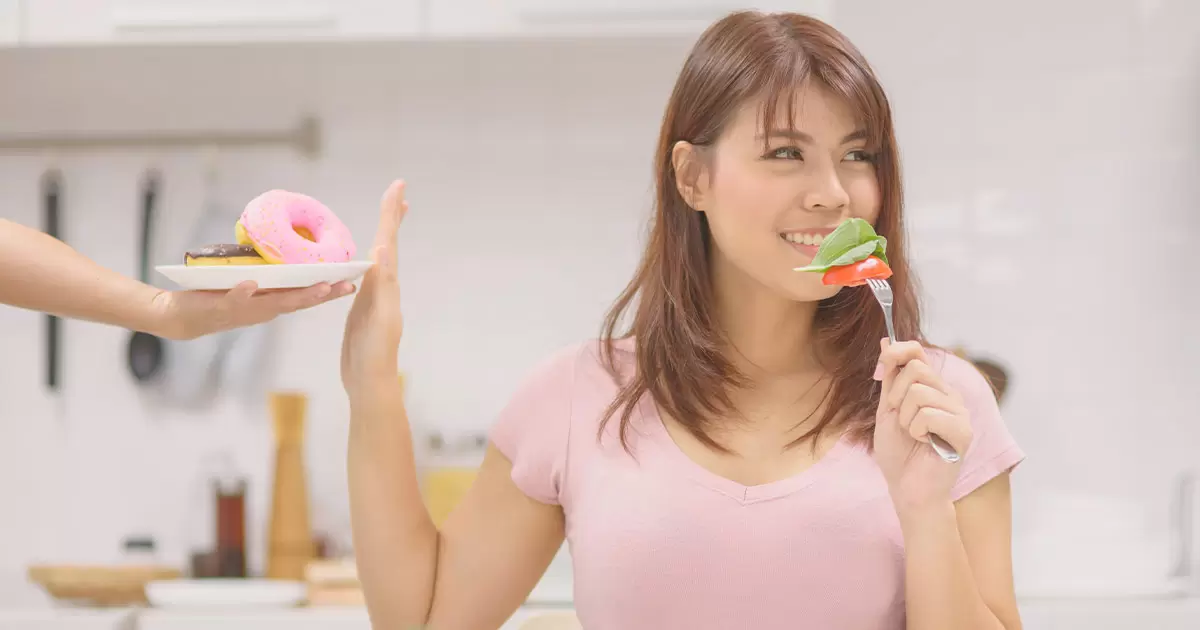
Self-control also called willpower, refers to the “ability to regulate one’s emotions, behaviors and desires through conscious effort”. Having strong self-control correlates with:
- Better Health – Less smoking, overeating, and risk-taking yields longevity benefits.
- Success at School/Work – Self-controlled individuals earn higher degrees, and incomes due to focus, and perseverance .
- Quality Relationships – Regulating anger/emotions fosters closeness, and cooperation more than impulsivity.
Developing robust self-control takes practice and applying techniques daily like an athlete building muscle.
Factors Influencing Self-Control
Biology, psychology, and social factors impact our capacity for self-regulation:
- Willpower as a Limited Resource – Tasks requiring much executive function drain finite cognitive reserves faster [5].
- Stress Hormones – Cortisol release under pressure weakens resolve more than relaxation which restores control [6].
- Genes and Early Life Experiences – Certain genotypes and childhood environments affect self-discipline into adulthood.
- Social Norms – Susceptibility to temptation versus integrity depends partly on example set by community [8].
Optimizing relevant factors empowers greater control over inner impulses through lifestyle adjustments.
Developing Impulse Control
Regulating urges requires concrete plans beating in-the-moment indulgence:
Pre-Commitment – Decide today’s behavior in calmer moments before temptation hits, such as meal prepping to avoid unhealthy drive-thru.
Temptation Bundling – Pair unhealthy urges with good habits, like exercising after work instead of snacking mindlessly.
Habit-Stacking – “Nest” new routines within existing automatic rituals, like packing vitamins each night with dental routine.
Cravings-Reframing – Challenge urge-thoughts by noting triggers’ transience and prioritizing priorities over fleeting gratification.
Delaying Gratification – Withstand initial impulse by waiting periods to thoughtfully evaluate true wants versus passing fancies.
Implementing routines above develops decisive conviction over fleeting desires. Consistency forms new automatic responses.
Mastering Emotions:
Emotions powerfully influences choices even for disciplined individuals:
Utilize Mindfulness – Noting feelings non-judgmentally through breathing exercises defuses impulses better than suppressing emotions.
Reframe Irrational Thoughts – Challenging assumptions linking feelings to events/triggers with rational perspectives regains equilibrium.
Manage Stress – Exercise, vacations, hobbies loosen tension’s grip weakening willpower through pleasure’s resilience boost.
Set Emotional Boundaries – Limit interactions with volatile personalities whose outbursts diminish your self-control through drained emotional reserves.
Regular mindfulness meditation most reliably transforms fleeting emotions from reasoning foes to allies bolstering resolve long-term.
Achieving Goals through Determination
Beyond resisting temptation, summon willpower productively through:
Portion Control – Gradual reductions in intake keep goals sustainable versus deprivation sparking rebound.
Losing the Battle, Not the War – Learn from slips without derailing overall progress through forgiving framesets.
Focus on Outcomes, Not Perfection – Celebrate directional progress over harsh scrutiny which demotivates through nitpicking.
Enlist Support Systems – Share aspirations constructively with caring groups keeping you accountable through thick/thin.
Handle Setbacks Strategically – View minor hurdles objectively and get back on track rather than giving up completely on goals.
Achieving ambitious aims requires perseverance through diligent daily effort over visible overnight transformations.

Supporting Self-control Development
Some additional strategies support enhanced self-discipline over the long term:
Cultivate a Growth Mindset – Believe willpower improves with practice through perseverance rather than a stable trait limiting potential.
Track and Reward Successes – Noting triumphs in journals encourages continued progress through visualization and intrinsic incentives.
Forgive Yourself Kindly – Accept past errors without condemnation to escape rumination’s focus leaked from present goals.
Consider Professional Help – For recurring bingeing/addictions undermining control over major durations despite tried strategies, therapy aids change.
Limit Unhelpful Influencers – Time with companions prone to gossip/instability deplete reserves whereas uplifting company restores fortitude.
FAQs: How to develop Self-control
Q: How long does it take to improve Self-control?
A: Comparable to forming any new routine or skill, strengthening self-control necessitates consistent practice of strategies over weeks or months. Maintaining patience and continuing small initiatives are significant.
Q: What if lack of Self-control feels like a character flaw?
A: Many consider self-control partly inborn, but exploration shows it can evolve through customs and outlook changes. Treating mistakes kindly allows refocusing energy on present aims.
Q: Does Self-control clash with enjoying life?
A: Techniques like allotting occasional planned indulgences, scheduling leisure time and ceasing perfectionism about minor lapses help self-control coexist with relaxation and amusement.
Q: How can busy schedules accommodate Self-control development?
A: Even with duties, priorities sorting, planning and routine-forming can still subtly include self-control cultivation like brief workouts or meal prep on weekends.
Q: When should professional assistance be considered for Self-control?
A: For persistent difficulties impairing welfare regardless of tried strategies, therapy or programs may aid individualized solutions, particularly concerning severe conditions.
Q: How do introverts better Self-control?
A: Personality impacts some tactic suitability, but all can benefit through self-knowledge, priority-setting, supportive accountability and way of life modifications at an individually sustainable pace.
Conclusion: How to develop Self-control
In reflecting on the extensive How to develop Self-control guide provided, the significant takeaway is that bettering willpower necessitates a dedicated and thoughtful process over both the short-term and long-haul. While impacted by factors outside individual control like biology and environment, everyday efforts can fortify this vital life ability essential for health, ties, and accomplishment.
Similar to physical fitness, cultivating Self-control demands constructing strategies, routines and viewpoints tailored to individual temperaments, assistance systems and goals in order to enact positive modification step-by-step and sustainably. how to develop Self-control is a journey necessitating determination through successes and setbacks the same.
Looking ahead, how to develop Self-control, continuing to refine tactics, track advancement and reward one constructively paves the way toward exercising even greater control productively serving highest priorities. Though not a fast remedy, generating Self-control development an ongoing concern brings behaviors into tighter alignment with core concepts and visions for an authentically purposeful life lived according to personal meaning of welfare, connection and fulfillment.
In conclusion, how to develop Self-control fostering willpower centers on exercising thoughtful care for self and others through regularly bettering inner restraint’s manifestation. While keeping reasonable anticipations, dedicating to this work unleashes tremendous untapped potential to form each moment and ultimately make the most of the valuable present of time. May this guidance offer a initial point for persons to initiate realizing enhanced authority over self by patience, compassion and stalwart venture.