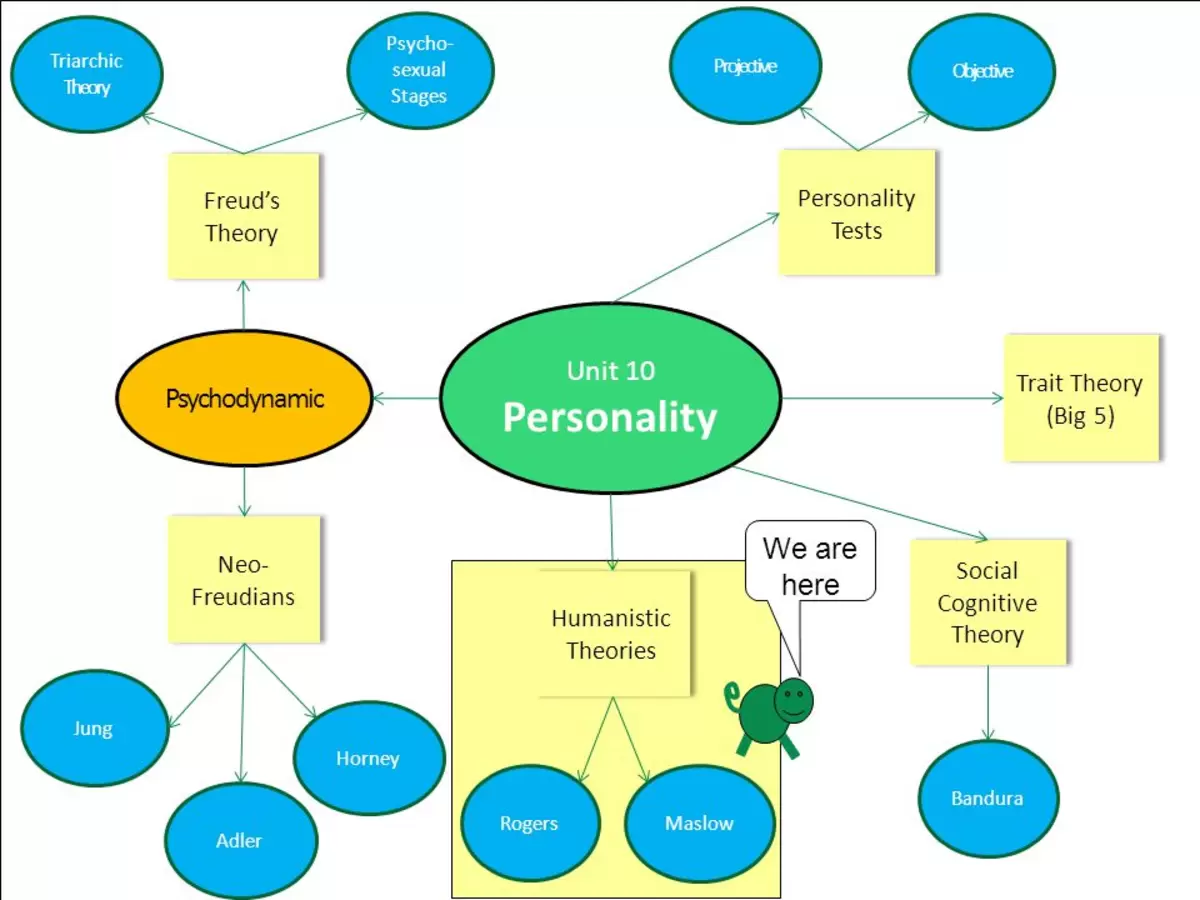
Who developed the first comprehensive theory of personality
When examining the history of personality theory, most scholars point to Gordon Allport as having developed the first comprehensive theoretical model to systematically explore the Concept of personality.
Allport’s seminal 1937 work Pattern and Growth in Personality laid the groundwork for the modern scientific field of personality psychology. In it, he defined personality as “the dynamic organization within the individual of those psychophysical systems that determine his unique adjustments to his environment.”
This represented the first articulate formulation of personality as a unified, multidimensional construct. Allport delved into recognizing both situational and dispositional influences on behavior. He also distinguished between cardinal traits, which strongly influenced behavior across situations, versus secondary traits which had less impact.
Building on earlier philosophers’ ideas around temperament and character, Allport was the first theorist to assemble a wide-ranging, empirically-supported theoretical framework for examining personality as an intertwined construct. His work initiated the ongoing scientific endeavor to understand how innate qualities interact with experience and context to shape individuals’ characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling and acting.
In developing the earliest comprehensive taxonomy of traits and empirically studying their structure and impacts, Allport unequivocally established the foundation upon which modern personality psychology and all subsequent models were built. For this legacy, he is rightly credited as having developed the first fully articulated, scientifically-validated conception of personality as a multidimensional phenomenon.
This post explores influential theorists who paved the way for modern understanding of the “who developed the first comprehensive theory of personality”.
Early Philosophical Conceptions
Hippocrates (460-370 BCE) first associated temperament types with fluid balances. Aristotle (384-322 BCE) saw virtues as habitual behaviors shaping character.
Carl Jung and Depth Psychology
Jung expanded Freudian drive concepts, theorizing archetypes forming our “collective unconscious”. His work influenced Myers-Briggs Type Indicator assessments.
Gordon Allport’s Trait Approach
Allport’s 1937 book established trait concepts as fundamental to individual personalities. He categorized traits as cardinal vs secondary. Hundreds of studies have since supported trait dimensionality.
Hans Eysenck’s Biological Modeling
Eysenck’s arousal-based model measured individuals along extroversion/introversion and neuroticism scales. He linked these to genetics, sparking the five-factor model.
Walter Mischel and Situationism
Mischel critiqued trait theory’s inability to predict behavior across contexts. His 1968 book highlighted behavior as interacting traits with situations rather than fixed dispositions.
While predecessors contemplated character, Allport’s trait approach served as the first comprehensive empirically-founded framework for the psychology of individual differences. Subsequent theorists built from this foundation to develop richer models addressing its limitations.
Conclusion- Who developed the first comprehensive theory of personality
Allport’s groundbreaking 1937 work laid the foundation for answering the question “who developed the first comprehensive theory of personality?” By developing coherent empirically-based concepts of traits, dispositions, and their interaction with environment – combined with rigorous studies providing supportive evidence – Allport established personality psychology as a quantitative science.
Predecessors provided scattered philosophical speculation, but Allport was uniquely responsible for conceptualizing personality as an organized, measurable construct and systematically fleshing out its nature through research. His work enabled subsequent founders like Eysenck, Jung and Mischel to build upon established principles in forging newer models.
While viewpoints have evolved, Allport ensured later theories were built upon a strong evidence-based starting point for understanding personality as an intricate multi-faceted phenomenon. Through his seminal volume, he earned the singular distinction of having undertaken the arduous challenge to methodically construct personality psychology’s first thorough empirical theory – a legacy cementing him as the answer to “who developed the first comprehensive theory of personality?”. Allport’s theory removed personality from the realm of abstract speculation into scientific framework, permanently changing the trajectory of the field.
FAQs: Who developed the first comprehensive theory of personality
What Was Allport’s Key Work Developing This Theory?
Allport’s 1937 book “Pattern and Growth in Personality” represented the first systematic effort to develop a taxonomy of traits and conceive of personality as a coherent theoretical construct.
How Did Allport Define Personality in His Model?
Allport defined personality as “the dynamic organization within the individual of those psychophysical systems that determine his unique adjustments to his environment.” This established personality as a multi-dimensional phenomenon.
What Trait Distinctions Did Allport’s Theory Propose?
Allport differentiated between cardinal traits that strongly influenced behavior, versus secondary traits with less situational consistency. This dimensionality aspect proved influential in later five-factor models.
How Did Allport Gather Empirical Evidence?
Beyond conceptual theory-building, Allport undertook rigorous quantitative studies assessing traits’ structure and impacts – a hallmark of a modern scientific approach that set his work apart.
How Did Allport’s Concepts Shape Later Theories?
Foundational principles from Allport’s model enabled subsequent personality psychologists like Eysenck, Jung and Mischel to build formal quantitative models expanding understanding of traits and their interaction with environment.